Rotating Shift Schedules Explained: Pros, Cons, and Best Practices


Rotating shifts are work schedules where employees cycle through different shift times (day, evening, and night) according to a predetermined pattern, rather than working consistent hours every week. This scheduling approach impacts millions of workers across industries that require 24/7 operations, from hospitals and manufacturing plants to emergency services and customer support centers. Research shows that 15-33% of the working population engages in shift work, with healthcare workers representing one of the largest affected groups.
Managing these scheduling issues isn't simple. Managers must balance continuous coverage while keeping their workforce healthy and satisfied, which takes skill and the right tools. Let's face it, we've all experienced the frustration of missed communications or last-minute schedule changes. This guide breaks down effective rotating shift patterns like DuPont and Pitman schedules, addresses real health and legal considerations, and provides practical strategies that actually work.
What Is a Rotating Shift? Quick Definition
A rotating shift is a work schedule where employees cycle through different shift times (day, evening, and night) according to a predetermined pattern, rather than working the same hours every day. Think of it this way: you might work from 7 a.m. to 3 p.m. one week, shift to 3 p.m. to 11 p.m. the next week, and then work 11 p.m. to 7 a.m. the following week before the cycle repeats.
The idea remains simple: ensure continuous operational coverage while distributing both desirable and less desirable shifts fairly among all staff members. This approach prevents any single employee from getting stuck with unpopular hours like nights or weekends, while your business maintains full coverage around the clock.
How Rotating Shifts Work
These schedules operate on a systematic cycle where employees move through different shift times according to predetermined patterns. Instead of working the same hours every day, workers alternate between day, evening, and night shifts over weeks or months. This distribution ensures no one permanently works the least desirable hours.
Most rotating shifts use either 8-hour or 12-hour shifts, with employees cycling through different time slots. For example, you might work 7 a.m. to 3 p.m. for one week, then switch to 3 p.m. to 11 p.m. the following week, and finally move to 11 p.m. to 7 a.m. for the third week before the cycle starts again.
This system helps businesses run 24/7 without burdening specific employees with permanent night or weekend shifts. The cycle distributes both good and bad hours among all staff members, creating fairness while ensuring coverage during all operational hours. Companies also benefit from cross-training, as employees gain experience working during different shifts when various tasks typically occur.
Slow vs. Fast Rotation in Rotating Shifts
Slow rotation systems keep employees on the same shift for 1-4 weeks before changing, giving your body more time to adapt to each schedule. This approach allows your internal clock to partially adjust to the new sleep-wake cycle, potentially reducing fatigue associated with shift changes. Industries like manufacturing and chemical plants often prefer slow rotation because it provides stability for complex operations requiring specialized knowledge.
Fast rotation changes shifts every 2-3 days, preventing your body from fully adapting to any particular schedule. While this sounds disruptive, it actually prevents complete adaptation to unusual sleep patterns, which helps when returning to normal schedules. Emergency services and healthcare facilities sometimes use fast rotation to ensure all staff members share the challenges of night shifts equally.
Forward vs. Backward Rotation
When designing schedules, direction matters more than most managers realize. Forward rotation moves clockwise through the schedule: day shifts progress to evening, then to night shifts. Backward rotation does the opposite, moving counterclockwise from night to evening to day shifts.
Your body's internal clock strongly favors forward rotation. This clockwise pattern aligns with natural circadian rhythms, making it easier for employees to gradually delay their sleep time rather than advance it. Medical research consistently shows forward rotation reduces sleep disruption and minimizes chronic fatigue that builds up over weeks of schedule changes.
The health difference is substantial. Forward-rotating schedules reduce cardiovascular and metabolic health risks compared to backward rotation, particularly for employees who maintain these schedules long-term. Each shift change in a forward pattern requires only a few hours of sleep adjustment, while backward rotation forces the body to fight against its natural rhythm.
Despite these clear benefits, some organizations still implement backward rotation for operational reasons. Manufacturing plants might need their most experienced supervisors on night shifts, requiring them to rotate backward from day positions. Similarly, restaurants often rotate backward because their busiest periods demand senior staff during evening and weekend shifts. If your operational needs allow flexibility, forward rotation consistently produces better employee outcomes and lower absenteeism rates.
Common Rotating Shift Patterns Explained
Different patterns exist to balance business needs with employee wellbeing. Your choice depends on industry requirements, staffing levels, and company culture. These popular shift patterns create predictability for employees while ensuring continuous coverage. The right pattern improves both productivity and employee satisfaction.
DuPont Schedule (4-on/3-off/3-on/1-off/3-on/3-off)
The DuPont schedule runs as a complex 4-week cycle with 12-hour shifts, giving employees seven consecutive days off during each rotation. The pattern works like this: 4 days on, 3 days off, 3 days on, 1 day off, 3 days on, 3 days off. Chemical plants and manufacturing facilities favor this schedule where operations never stop.
The biggest advantage? Those extended blocks of time off provide substantial recovery periods. The downside hits during that single day off in the middle of the cycle; it feels insufficient. The 12-hour shift length can also wear down employees physically over time.
Pitman Schedule (2-2-3)
The Pitman schedule, also known as the 2-2-3 pattern, runs on a 2-week cycle with 12-hour shifts: work 2 days, off 2 days, work 3 days, off 2 days, work 2 days, then 3 days off.
The real draw here is that three-day weekend every other week. Unlike other rotations that scatter days off randomly, this pattern creates predictable extended breaks that actually let people plan vacations, maintain relationships, and recover from those long 12-hour stretches. Healthcare and public safety sectors use this rotation because it acknowledges reality: 12-hour shifts demand a lot from workers, and people need real recovery time, not just single days off that disappear into errands and catch-up sleep.
2-2-3-2-2-3 Rotating Shift Pattern
The 2-2-3-2-2-3 schedule builds on the Pitman pattern but stretches over multiple weeks with 12-hour shifts. Employees work two days, rest for two days, work three days, rest for two days, work two days again, then get three consecutive days off before starting over.
This pattern prevents anyone from working more than three days straight, which cuts down on fatigue while keeping your facility fully staffed around the clock. The extended weekends every other cycle give employees real recovery time, something that traditional schedules struggle to provide.
Healthcare facilities, manufacturing plants, and emergency services use this approach because it delivers predictable time off while spreading the workload evenly. Employees appreciate those regular three-day breaks, and employers see the benefits through reduced burnout and lower turnover. The rotating nature means everyone takes their turn with day shifts and night shifts, ensuring no one gets permanently stuck with the less popular hours.
Southern Swing Rotating Shift
The Southern Swing schedule takes a different approach than most rotation patterns. Employees work seven straight day shifts, get two days off, work another seven day shifts, take two more days off, then switch to seven night shifts followed by three days off. This pattern uses four teams on standard eight-hour shifts instead of the longer 10-12 hour shifts found elsewhere.
Public safety departments and healthcare facilities use this schedule because those week-long stretches on each shift type give your body a real chance to settle into a rhythm before everything changes again. The three-day weekend after night shifts becomes crucial for recovery, and the shorter eight-hour shifts don't leave you completely drained like extended shifts can.
The trade-off? Those seven-day stretches can start feeling long, especially toward the end. Your circadian rhythm still takes a hit when you flip from days to nights, even with that recovery time built in. But many organizations find the week-long consistency makes the adjustment period more manageable than constantly switching every few days.
This pattern works particularly well for teams that need deep familiarity with their shift's unique demands. Day shifts handle different situations than night shifts, and having a full week to master each environment can improve both performance and job satisfaction.
Other Variations of Rotating Shifts (Continental, Panama, 3-2-2-3)
Several other rotation patterns address specific workplace needs. The Continental shift creates rapid rotation where employees switch shifts every 2-3 days. Your body never fully adapts to any schedule, but you also avoid getting stuck in permanent night shift patterns.
The Panama schedule alternates between 2-day and 3-day work blocks with matching time off. Manufacturing companies favor this approach because it balances intense work periods with solid recovery time. The 3-2-2-3 pattern delivers predictable long weekends: three days on, two off, two on, three off.
Emergency services, utilities, and manufacturing operations rely heavily on these variations. Most organizations create hybrid schedules by mixing elements from different patterns or building custom rotations that fit their workforce size and operational demands, solving specific business challenges through thoughtful schedule design.
Industries & Roles That Use Rotating Shifts
Rotating schedules power the backbone of our 24/7 economy, from the hospital where your family receives emergency care to the power plant keeping your lights on. These industries can't hit pause. They need continuous coverage to serve customers, maintain safety, and keep critical processes running.
Healthcare leads the pack, with hospitals and emergency services staffing nurses, physicians, technicians, and support teams around the clock. Most healthcare professionals work 12-hour shifts following Pitman or 2-2-3 patterns, while paramedics and hospital security teams cycle through rotations that guarantee immediate response when seconds count.
Manufacturing facilities maximize equipment use and production targets through continuous coverage. Machine operators, supervisors, maintenance techs, and quality inspectors choose DuPont or Southern Swing schedules to keep assembly lines, chemical processes, and quality control running without interruption.
Public safety never sleeps. Police departments, fire stations, and 911 dispatch centers protect communities through carefully planned rotations. Officers and firefighters often work 24-hour shifts followed by extended recovery time, while dispatchers cycle through patterns that maintain emergency response capability during every hour of every day.
Transportation and logistics keep global commerce moving through airport operations, railway systems, trucking dispatch, and shipping facilities. Air traffic controllers guide planes through busy airspace, baggage handlers process thousands of pieces daily, and freight coordinators manage shipments across time zones. All these roles require continuous coverage to match demand.
Energy and utilities deliver uninterrupted service through power plants, water treatment facilities, and grid monitoring stations. Plant operators monitor complex systems, control room technicians track performance metrics, and maintenance crews perform critical repairs during scheduled rotations that prevent service disruptions.
Pros & Cons of Working Rotating Shifts
Rotating schedules present significant trade-offs that affect both employees and organizations. Understanding these advantages and drawbacks helps managers develop strategies to maximize benefits while addressing potential challenges. The impact varies widely among individuals based on factors like age, health status, family circumstances, and personal sleep patterns. What feels manageable for one person might prove exhausting for another, making it crucial to consider unique situations when evaluating opportunities.
Advantages for Employees
Working rotating schedules offers several compelling benefits that can enhance both earning potential and work experience. Premium pay represents one of the most immediate advantages, as employers typically offer shift differentials for evening, night, and weekend hours. These premiums can add hundreds or thousands of dollars to annual wages.
The fairness factor creates another significant benefit. Unlike fixed schedules where certain employees get stuck permanently on night shifts, rotation systems ensure everyone shares both desirable and less popular hours. This equitable distribution prevents resentment and creates a more cohesive team environment.
Changing schedules also provide varied work experience as different operations occur during different shifts. Day shifts might focus on administrative tasks, while night shifts handle maintenance or different production requirements. This exposure broadens skill sets and increases value to employers.
Extended blocks of time off represent another major advantage. Many rotation patterns, like the DuPont schedule, provide several consecutive days off that feel like mini-vacations. These longer breaks allow for better recovery and more meaningful personal time than traditional schedules offer.
Advantages for Employers
Organizations benefit significantly from implementing rotating shift schedules across multiple operational areas. Continuous operations become possible without coverage gaps, ensuring customer service and production continue around the clock. This consistency translates directly to improved revenue potential and customer satisfaction.
Equitable distribution of shifts helps maintain team morale and reduces turnover. Implementing effective employee engagement strategies, such as real-time feedback, can further boost satisfaction. When everyone shares the burden of less desirable hours, workplace fairness improves dramatically. This approach prevents the resentment that builds when certain employees feel stuck with permanent night or weekend assignments.
Cross-training opportunities emerge naturally as employees gain exposure to different aspects of the business during various shifts. Workers develop broader skill sets and better understanding of operations, creating more versatile team members who can adapt to changing needs.
Properly managed schedules can also reduce overtime costs. With adequate staffing across all shifts and strategic scheduling, organizations avoid the premium payments associated with emergency coverage or extended hours. This financial benefit compounds over time, especially in industries with high overtime rates.
Legal & Compliance Considerations
Rotating shifts bring legal complexities and potential workplace hazards that can trip up even experienced managers. Schedule conflicts can arise when laws mandate specific rest periods or advance notice requirements. When you get these requirements right from the start, you save yourself from expensive violations and actively protect your workforce.
The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) covers your basic obligations. It doesn't dictate shift patterns, but it demands overtime pay for non-exempt employees working more than 40 hours weekly. This becomes tricky when employees switch between shifts in the same pay period; your timekeeping systems must track hours accurately across all rotations to comply with salary overtime laws.
State laws add another layer of complexity. Predictive scheduling laws in California, Oregon, and New York City require advance notice of work schedules. Some states mandate specific rest periods between shifts. Washington State requires shift premium pay even during authorized leave periods.
Industry-specific regulations create additional hurdles. Healthcare facilities face restrictions on mandatory overtime for nurses, while transportation companies must follow hours-of-service regulations designed to prevent fatigue. These sector-specific rules often trump general labor laws.
Union agreements deserve special attention since they frequently include detailed provisions about shift scheduling, premium pay, and rotation patterns. Unions and management negotiate these terms to usually offer more generous benefits than minimum legal requirements.
Regulators continually update the compliance landscape, with increasing focus on predictable scheduling and worker well-being. Stay current by regularly consulting legal counsel and industry associations to maintain compliant policies.
Actionable Tips for Managers & Schedulers
Managing rotating shifts effectively comes down to strategic planning and rock-solid communication. Start with forward rotation patterns whenever you can, moving clockwise from day to evening to night shifts. Your employees' bodies will thank you since this direction works with their natural sleep cycles instead of fighting against them.
Give your team advance notice—a key shift change best practice. A minimum of two to four weeks allows people to arrange childcare, plan family time, and mentally prepare for shift changes. This isn't just courtesy. It directly impacts whether people show up ready to work or call in sick because they couldn't manage their personal lives around last-minute schedule changes.
Make scheduling collaborative, not dictatorial. Regular check-ins help you understand who needs morning shifts for school drop-offs, who prefers nights for personal reasons, and where potential conflicts might arise. When your team has input on rotation patterns, they will far more likely work challenging shifts without complaints or high turnover.
Skip the fancy scheduling software promises and focus on communication that actually works. While complex platforms handle the logistics, text messaging solves your real daily challenges. Unlike email that sits unread, people read SMS immediately. When you need to alert the night shift about a safety issue or notify day workers about schedule changes, text messages reach everyone instantly and create real two-way communication between shifts.
Train your supervisors to recognize fatigue and establish solid handover procedures between rotations using standardized shift report formats. Regular reviews of productivity numbers, employee feedback, and basic health indicators help you adjust rotation patterns before problems become crises. The goal isn't just operational coverage. You want to build a culture that acknowledges shift work challenges while maintaining performance standards.
Common Misconceptions & FAQs About Rotating Shifts
When it comes to rotating shifts, you'll encounter plenty of myths and half-truths that can cloud your judgment as a manager or employee. These misconceptions often stem from outdated information, limited personal experience, or generalizations that don't account for modern scheduling practices and individual differences. Understanding what's actually true about shift work helps you make better decisions and implement more effective strategies.
Myth Debunking
One of the most persistent myths is that these schedules always hurt productivity. In reality, well-designed patterns can boost productivity by up to 20% compared to fixed schedules. The key lies in proper implementation—forward rotation patterns, adequate rest periods, and employee input all contribute to maintaining high performance levels. When you expose workers to different tasks and responsibilities across shifts, you create more versatile, engaged employees who bring fresh perspectives to their work.
Another common misconception is that these schedules inevitably lead to lower job satisfaction. While some employees struggle with irregular hours, many workers actually prefer the variety and flexibility that changing shifts provide. The ability to share both desirable and less popular time slots fairly often increases overall team morale. Employees appreciate not being permanently stuck with night shifts or weekend work, and the variety prevents the monotony that comes with doing the same job at the same time every day.
Perhaps the most dangerous myth is assuming all employees adapt to shift changes equally well. Individual tolerance varies dramatically based on factors like age, health status, family responsibilities, and personal sleep patterns. Younger workers often adjust more easily, while older employees may struggle with circadian disruption. Some people are natural night owls who thrive on evening shifts, while others are morning people who perform best during day hours. Smart managers recognize these differences and work to accommodate individual needs whenever possible.
Many people believe night shifts carry the same health risks as day shifts. The science clearly shows that night work creates more significant physiological challenges, including disrupted sleep patterns, increased cardiovascular risks, and metabolic concerns. This doesn't mean overnight hours are impossible to manage safely, but it does mean you need specific strategies to protect worker health during these times.
Frequently Asked Questions
How are rotating shift schedules typically managed effectively?
Modern shift management relies heavily on scheduling software that automates pattern creation and tracks employee preferences. Successful managers provide schedules at least two weeks in advance, allowing workers to plan their personal lives around work commitments. The best systems incorporate employee input through surveys or feedback sessions, creating schedules that balance operational needs with worker preferences. Clear communication becomes essential—when schedule changes occur, you need reliable ways to reach every employee quickly, regardless of which shift they're currently working.
What are the main health implications of rotating shifts, and how can they be managed?
Changing shift patterns can disrupt your natural sleep cycles, potentially leading to cardiovascular issues, metabolic disorders, and mental health challenges over time. Research shows increased risks for diabetes, heart disease, and mood disorders among long-term shift workers. However, you can minimize these risks through forward-rotating schedules, maintaining consistent sleep routines even on days off, creating sleep-friendly environments at home, and regular health monitoring with healthcare providers familiar with shift work challenges.
Are there financial advantages to working rotating shifts?
Yes, these schedules typically come with premium pay in the form of shift differentials. Evening and night shifts often pay 10-15% more than day shifts, and weekend work frequently includes additional compensation. These financial incentives help offset the challenges of irregular schedules. Some rotation patterns also provide longer consecutive days off, which can reduce commuting costs and allow for better work-life balance without using vacation time.
How can employees best adapt to rotating shift schedules?
Successful adaptation starts with maintaining consistent sleep habits, even on your days off. Try to keep the same bedtime and wake-up time as much as possible. Create a dark, quiet sleep environment and avoid caffeine close to bedtime. Forward-rotating shifts are easier on your body than backward rotation, so advocate for clockwise patterns when possible. Stay connected with family and friends by communicating your schedule clearly, and don't hesitate to ask for support during difficult transitions between day and night shifts.
What communication challenges arise with rotating shifts, and how can they be addressed?
Communication becomes complex when your team works different hours throughout the week. Traditional email often fails because employees may not check it regularly across all shifts. Important updates can get lost when workers are transitioning between schedules. The most effective solution is implementing direct SMS communication that reaches employees instantly, regardless of their current shift pattern. This ensures critical information about schedule changes, safety updates, or operational news gets delivered and acknowledged promptly across all time periods.
Alternatives to Rotating Shifts
When rotating shifts don't align with your operational needs or workforce preferences, several alternative scheduling approaches can deliver the coverage you need while tackling specific business challenges.
Fixed shifts keep employees on consistent schedules that never change. Your day shift worker clocks in at 9 a.m. and leaves at 5 p.m. every single day, while night shift staff permanently work 11 p.m. to 7 a.m. This works particularly well for businesses with distinct operational needs at different times. Consider call centers serving global markets or manufacturing plants with specialized day and night operations. Fixed shifts eliminate the sleep disruption that comes with rotation, though they can create fairness concerns when some employees get permanently stuck with less desirable hours.
Split shifts break an employee's workday into two separate chunks with a significant gap between them. Restaurant workers might handle lunch rush from 11 a.m. to 2 p.m., disappear during the slow afternoon hours, then return for dinner service from 5 p.m. to 9 p.m. This pattern helps businesses match staffing to customer demand during peak periods while cutting labor costs during dead zones.
Compressed workweeks pack standard full-time hours into fewer days, such as four 10-hour shifts instead of five 8-hour ones. Manufacturing plants often embrace this approach to maximize equipment usage while rewarding employees with three-day weekends. The catch? Those longer daily shifts can wear people down faster.
Flexible scheduling hands employees some control over their start and end times within set boundaries. Tech companies and administrative offices frequently offer this perk to boost work-life balance and accommodate personal needs while keeping core collaboration hours intact.
Stay Connected Across Every Shift
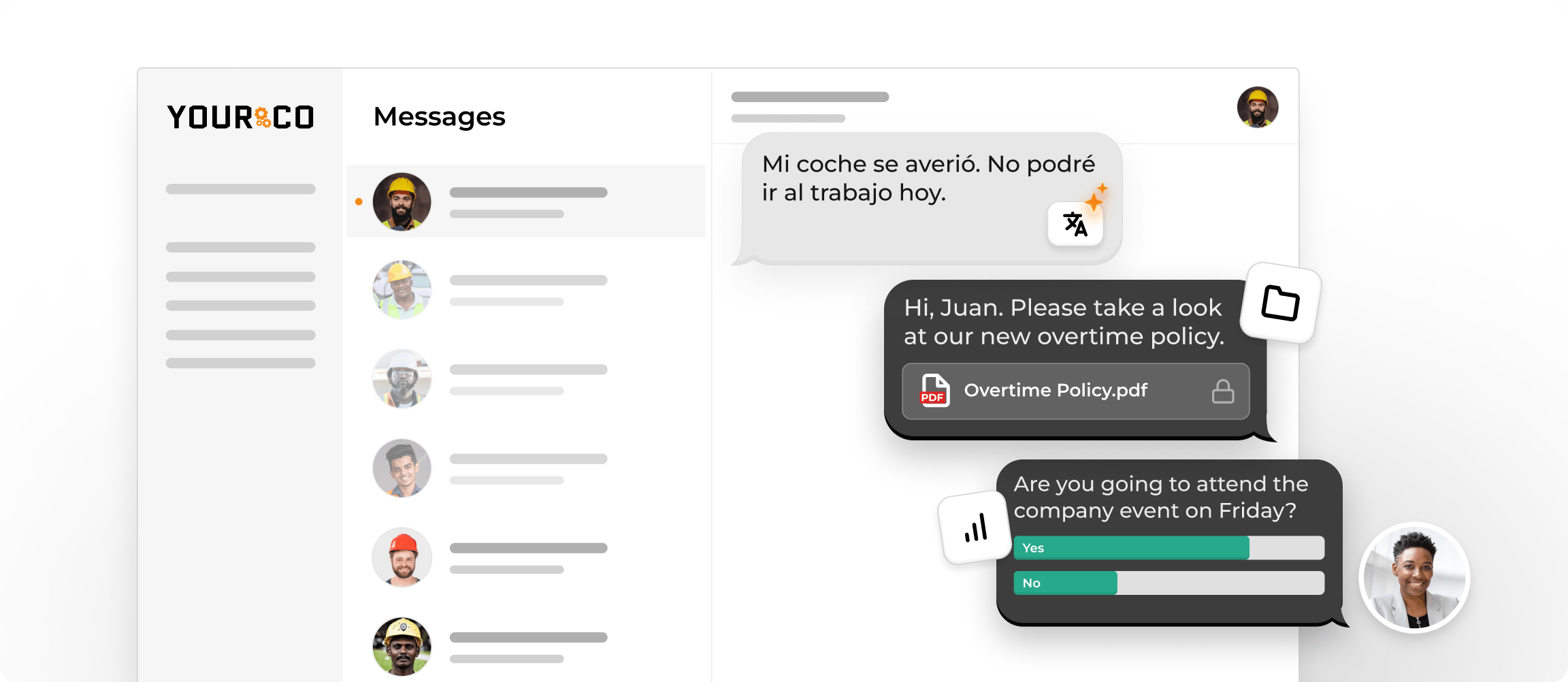
Rotating shifts create unique communication challenges that most managers underestimate. The biggest mistake? Assuming traditional communication methods work when your team operates across multiple time zones within the same building.
Your night crew can't attend morning meetings. Your weekend staff miss Monday announcements. Email chains become useless when responses come 16 hours apart. These aren't minor inconveniences. They represent operational gaps that lead to missed coverage, safety incidents, and frustrated employees who feel disconnected from the team.
Yourco's SMS platform solves this by meeting employees where they already are: their phones. When a day-shift supervisor needs to communicate urgent information to the incoming evening team, the message arrives instantly. Schedule changes, safety alerts, and coverage requests reach everyone simultaneously, regardless of their current rotation.
Additionally, Yourco’s AI-powered translation feature ensures that language barriers are no longer an obstacle. With the ability to communicate with employees in 135+ languages, you can connect with your diverse workforce and ensure that everyone, regardless of their language, stays informed and engaged.
The platform integrates with your existing scheduling systems, automatically sending reminders and updates without manual effort. You gain real-time visibility into who receives and responds to messages, eliminating the guesswork that plagues rotating operations. This direct connection prevents the communication breakdowns that naturally occur when teams work different hours, creating a more informed workforce across all rotations.
Try Yourco for free today or schedule a demo and see the difference the right workplace communication solution can make in your company.



