How To Make an Employee Attendance Improvement Plan


It's 5:00 a.m. and you're already juggling text messages from three employees calling out for the morning shift. Now you're scrambling to fill gaps, approving overtime you hadn't budgeted, and hoping the rest of the crew doesn't burn out. Moments like these show how quickly excessive absenteeism can drain productivity, dent team morale, and trigger compliance headaches.
Beyond the scramble, the business hit is real: wages paid for last-minute overtime, slowed output, and the quiet frustration of teammates shouldering extra work when excessive absences surface again and again. Culturally, repeated no-shows signal that showing up isn't important, eroding trust faster than any policy update.
This comprehensive guide walks you through building a practical attendance improvement plan that sets clear goals, gathers solid data, and balances accountability with support so attendance matters to everyone. You'll find step-by-step advice with actionable strategies you can start using today to keep shifts covered and teams engaged.
1. Define the Scope and Goals of Your Plan
An effective attendance strategy only succeeds when you set clear, measurable goals that everyone understands. Before you write a single action item, take a snapshot of where you stand. Pay attention to:
- Average absence rate
- Most common reasons
- The shifts that suffer the highest no-show numbers
These baseline metrics give you something concrete to improve upon.
Next, separate chronic absenteeism from one-off emergencies. A worker who calls out twice a year for a sick child needs a different approach than someone who misses every other Monday. This distinction keeps the process fair and focuses your energy where it matters most.
Now translate the numbers into a target. A strong SMART goal might read, "Cut last-minute shift call-outs by 20% in the next three months." Specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound—no one has to guess what success looks like, and progress is easy to track with weekly reports.
Write down why the strategy exists:
- To improve attendance
- To support employees
- To keep the operation running smoothly
Clear purpose statements help employees see the bigger picture and buy into the effort. Tailor the goal to the real issue—tardiness, no-shows, or early departures—so every metric, conversation, and follow-up meeting stays focused on the behavior you need to change.
2. Review Policies and Communicate Expectations
Employees can't follow rules they don't understand, so your first move is establishing a clear, consistent attendance policy that everyone can easily read. Building on your defined goals, this policy becomes the foundation for all improvement efforts.
Start by pulling the current rules off the shelf. Look for the basics:
- Paid and unpaid leave
- How to call out
- Required documentation
- What happens if someone no-shows
If any part feels vague, tighten it up. Clear policies might specify "Call your supervisor at least two hours before shift start" rather than simply saying "Give reasonable notice."
Translate legal or HR jargon into everyday language. Replace "unexcused absence" with "absence without prior approval," and skip long paragraphs in favor of short sentences or a quick Q&A format. Share the policy where people already look (break-room posters, onboarding packets, and text links in every schedule reminder), so no one has to hunt for it.
Consistency matters just as much as clarity. Apply the same standards across departments and locations, and document every exception. When employees see that rules are fair, they're more likely to trust the process and stick to it.
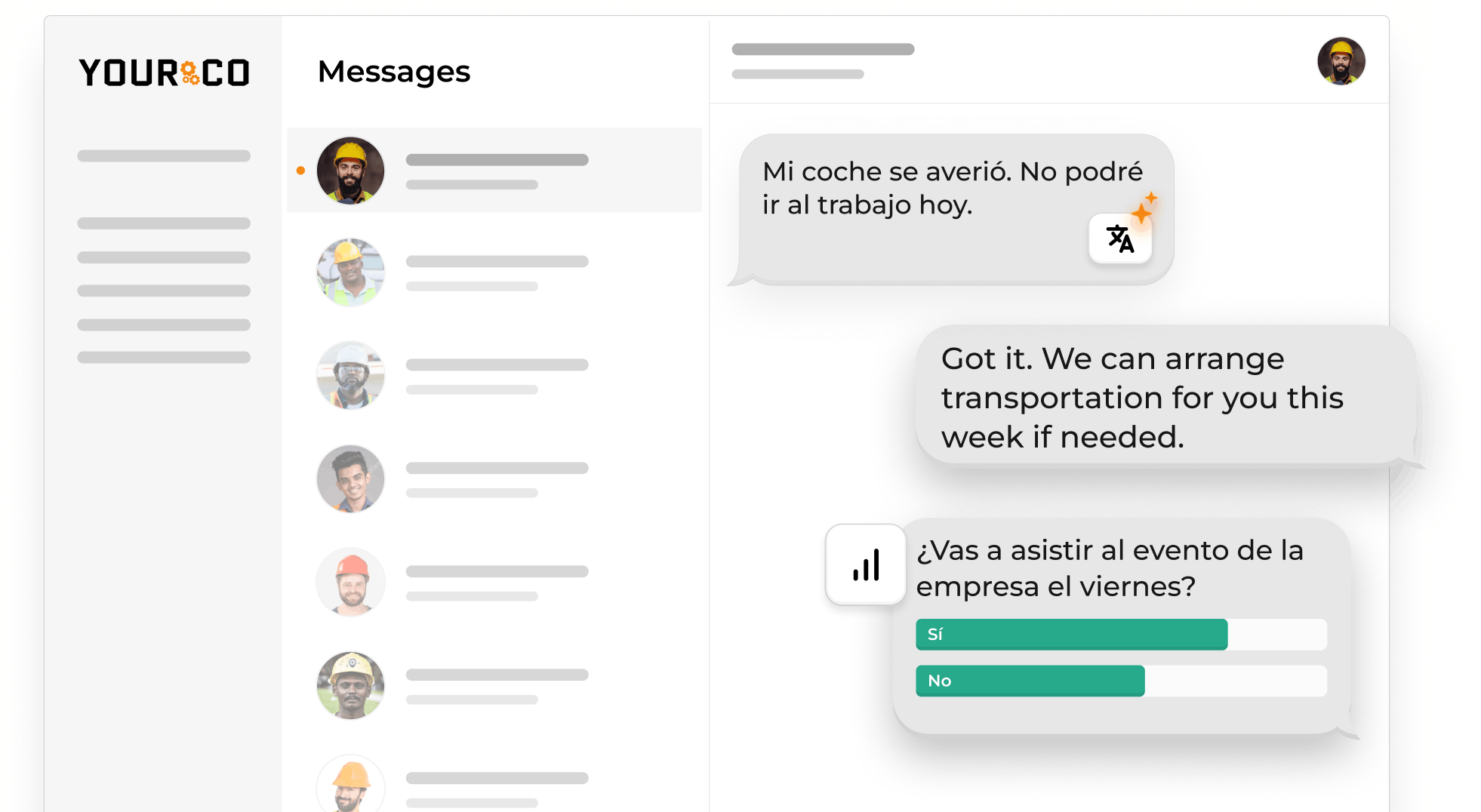
Non-desk crews need extra support. Short SMS reminders keep policies top of mind when workers clock in on a loading dock or retail floor. These resources ensure nothing gets lost between shifts, especially when communicating safety protocols and compliance updates.
3. Collect Attendance Data Consistently
You can't fix attendance problems until you track them the same way, every day, for every employee. With your policies clearly communicated, consistent data collection becomes the next critical step.
Start by choosing a reliable method that fits your workplace. Most teams rely on one of these proven options:
- Punch or swipe timecards for on-site crews who work from a fixed location
- Digital clock-ins through kiosks or tablets for flexible workspaces
- Supervisor reports for remote or field work where technology access varies
Pick one primary system and stick with it. When you mix methods, the data gets messy and creates disputes over hours and wages that nobody wants to deal with.
Next, decide whether you'll record presence (positive tracking) or only mark absences (negative tracking). Whatever you choose, stay consistent. Switching approaches halfway through makes it impossible to spot trends and damages trust with your team.
Document every absence the same way across all sites and shifts. Standard codes like tardy, no-show, or excused make reports easy to scan and remove guesswork when you need to have coaching conversations.
SMS makes this process much faster. A simple text link lets employees confirm they're sick, request a shift swap, or clock out when they finish a delivery route, creating a timestamped record without extra paperwork.
Finally, run a weekly data review. Most attendance software flags missing punches or duplicate entries automatically, which saves you from digging through spreadsheets and keeps your improvement efforts focused on reliable numbers.
4. Identify Root Causes of Absenteeism
Missed shifts rarely happen in a vacuum. If you treat every absence as simple rule-breaking, you'll chase symptoms while the underlying problem keeps spreading. Your attendance data provides the roadmap to uncover these deeper issues.
Start by mapping the patterns hidden in your logs. Look for clusters such as Monday call-outs, specific departments, or spikes during certain seasons. Scanning for trends by day, location, and employee group is the fastest way to flag systemic issues rather than isolated incidents.
Numbers alone don't tell the whole story, so pair the data with conversation. Short surveys, anonymous text polls, and one-on-one check-ins let employees explain why they're missing work—childcare gaps, unreliable transportation, burnout, or health concerns.
Treat these conversations as empathy interviews: ask open questions, listen more than you talk, and document themes without judgment. When staff feel safe to share, you uncover barriers you can address.
Culture and language can also mask root causes. In multilingual or non-desk teams, missed messages about shift changes are common. If employees never read policy emails, a no-show may stem from communication gaps, not attitude. Cross-reference attendance data with engagement scores or performance reviews—a dip in both often signals workload stress or poor scheduling fit.
Sort causes into two buckets:
- Issues the company can solve: adjusted start times, transportation support, wellness resources, communication barriers
- Issues the employee controls: habitual tardiness, personal time management, attitude problems
Tackling the first group shows good faith, making it easier to hold people accountable for the second. Address the cause, not just the calendar entry, and you'll see real, lasting gains in attendance.
5. Build Supportive Interventions
An attendance strategy only sticks when you pair clear rules with real help that makes showing up easier. Once you understand the root causes, you can design targeted interventions that address specific barriers.
Start by giving employees more control over their hours. Offering flexible scheduling options or a simple shift-swap process lets people handle doctor appointments, childcare, or sudden emergencies without disappearing on you. When transportation becomes the hurdle, a prepaid bus pass or coordinated carpool can turn a chronic latecomer into a reliable teammate.
Health issues drive many absences, so tackle them before they snowball into call-outs. Promote wellness days, on-site flu shots, or quick access to an Employee Assistance Program. Pair new hires or struggling staff with a buddy who can answer questions and model punctual habits. That way, mentorship feels personal, not punitive.
Tailor every intervention to what you learned in your root-cause analysis. If survey data shows burnout on the night shift, rotate duties or add a short paid break. When transportation becomes the hurdle, coordinate carpools or provide transit assistance. One size never fits all, and blanket fixes often miss the real problem.
Keep a simple record of what resources you provide so both you and the employee can track what's working. This shows good-faith effort and keeps conversations focused on solutions rather than blame.
6. Set Clear Action Steps for Employees
Employees need to know exactly what's expected of them, so your improvement strategy must lay out each step in plain language. This individual focus builds on the broader interventions you've put in place.
Begin with an initial meeting between you, the employee, and, when possible, HR. Use this conversation to review the attendance record, explain why it matters to the team, and agree on a path forward.
Create a written summary immediately after covering:
- Specific attendance issues discussed
- Clear improvement goals you're both aiming for
- Review dates when you'll check progress
- Consequences if attendance doesn't improve
Keep the goals quantifiable. For instance, you might agree that the employee will "arrive on time for at least 95% of scheduled shifts over the next 60 days." Setting clear targets makes success easy to track and removes ambiguity from the process.
Schedule brief check-ins—weekly at first, then bi-weekly as improvement holds. Use these sessions to review attendance data, celebrate wins, and troubleshoot obstacles. Document each meeting with simple notes: the date, key numbers, what's working, and what comes next.
Ask the employee to sign the improvement agreement. A signature confirms they understand the expectations, resources available, and potential consequences. By pairing measurable goals with consistent follow-through, you create a roadmap that supports the employee while protecting the business.
7. Monitor, Measure, and Adjust
An attendance improvement strategy only works when you keep it alive through routine check-ins, clear data, and quick course corrections. This ongoing monitoring ensures your individual action steps translate into lasting change.
Start by setting up regular review meetings—weekly for new initiatives, monthly once you see progress. A short meeting lets you and the employee look at the same numbers, celebrate wins, and catch problems before they get worse.
HR and the frontline supervisor both play important roles: HR keeps things fair across the company, while the supervisor gives daily feedback and understands what's really happening on the ground.
Use the same metrics you agreed on from the start—if the goal was "no more than two unexcused absences in 30 days," track exactly that. A shared dashboard or time-tracking tool keeps the data accurate and removes any confusion.
If progress stops, shift from asking "why didn't you show up?" to "what's getting in your way?" Then adjust the approach—maybe a different shift time, earlier reminders, or additional transportation help. Small changes show the employee you care while keeping the team covered.
Close the loop when it's time. When the employee hits the target for the full time period you set, document the success and move forward. If they don't meet the goal, follow the next steps you outlined from day one. Staying consistent turns the strategy from paperwork into real improvement.
8. Strengthen Ongoing Communication
Attendance climbs when people know what's happening and feel you have their back. This communication foundation supports all your monitoring and adjustment efforts by keeping everyone informed and engaged while promoting civility in the workplace.
Establish a steady rhythm of messages with shift reminders and automatic confirmations that cut down on last-minute call-outs. Quick three-question surveys can identify potential barriers, such as childcare or transportation issues, before they become absences.
Transparency matters just as much as timing. Share weekly highlights like "Absenteeism dropped 15% this quarter" so teams see their effort reflected in real numbers. Celebrate wins with recognition texts or extra breaks for crews that hit perfect attendance.
Enable two-way channels where employees can text back about plan changes, questions, or problems. This creates an open line for quick shift swaps instead of scrambling at shift start. For multilingual teams, platforms with auto-translation ensure Spanish-speaking drivers and English-speaking warehouse teams get the same clear message.
Keep language plain and consistent across all channels. Post printed short codes on notice boards, repeat them in texts, and translate key phrases. When everyone receives the same updates regardless of device or language, communication becomes a habit and attendance follows suit.
Ditch Scheduling Headaches with Yourco
We know how exhausting it is when call-outs hit at the worst possible moment. Clear expectations, consistent monitoring, genuine support, and steady communication form the foundation of any attendance strategy that works.
Yourco simplifies this entire process by reaching every employee instantly, regardless of their device or location. Send multilingual shift updates, deadline reminders, or policy clarifications straight to any phone—no app downloads or password resets needed. When crew members need to request shift swaps or report call-outs, two-way messaging eliminates the phone tag that usually eats up your morning.
Ready to turn last-minute scrambles into smooth operations? Try Yourco free today or schedule a demo and see the difference the right workplace communication solution can make in your company.
Frequently Asked Questions
What's the difference between an attendance improvement plan and disciplinary action?
An improvement strategy focuses on coaching and support with clear goals, regular check-ins, and practical help like flexible shifts. Disciplinary action follows formal company processes with warnings or suspension when previous efforts haven't worked.
What happens during an ICE I-9 inspection?
ICE begins with a Notice of Inspection, giving you at least three business days to produce forms. After reviewing your documentation, you may receive anything from a compliance letter to a Notice of Intent to Fine. Technical errors get a 10-day correction period, but substantive violations can result in immediate penalties. For complete details on the inspection process, consult the official ICE factsheet.
How long should an attendance improvement plan last?
Most strategies work best at 30, 60, or 90 days, depending on complexity. Quick fixes need 30 days, while complex issues involving childcare or medical appointments often need 90 days. Always set clear end dates and mid-point check-ins.
What's the supervisor's role in enforcing the plan?
Supervisors handle daily follow-up: tracking attendance, noting call-outs, and having brief supportive conversations. Document every interaction with dates and next steps. Regular check-ins work better than surprise meetings about problems.
How can companies support non-desk employees who struggle with attendance?
Use communication that reaches them: send shift reminders by text, use simple language in multiple languages, and create pocket cards with key policies. Remove barriers that cause absences with shift trading, childcare resources, or transit support.
What tools make it easier to monitor attendance consistently?
Look for systems that automatically capture time and send instant alerts. Digital time clocks with SMS notifications can flag no-shows within minutes. Platforms that save every message create clear records and reduce disputes during compliance audits.