Are Workplace Documents Required to Be in English? A Guide for Employers


Managing documentation in multiple languages can be challenging for employers, especially those with diverse, multilingual workforces. Clear communication is essential for workplace safety, operational efficiency, and employee morale.
When employees cannot fully understand their rights, responsibilities, or safety procedures, misunderstandings become more likely, productivity declines, and legal vulnerabilities increase.
This guide breaks down the legal requirements for workplace document language, explains the factors that influence your language choices, and provides practical strategies for maintaining compliance while keeping every employee informed.
Understand Essential Workplace Documents and Language Requirements
Language plays a pivotal role in maintaining effective operations and ensuring legal compliance. As workforces become increasingly diverse, the management of workplace documentation has evolved beyond simple record-keeping into a complex system that must bridge linguistic and cultural gaps while meeting various regulatory requirements.
Employers with multilingual workforces face several interconnected challenges:
- Bridging Linguistic and Cultural Gaps: Ensuring clear communication across diverse languages and cultures.
- Regulatory Compliance: Navigating varying legal requirements across regions and industries.
- Consistent Messaging: Maintaining uniformity in translated documents to prevent misunderstandings.
- Cultural Relevance: Adapting content to be culturally appropriate and easily understood.
For employers with multilingual workforces, the stakes are particularly high. According to the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission, language considerations in workplace documentation are often closely tied to protected characteristics like national origin, making this a critical area for careful management and compliance.
Know the Legal Requirements for Workplace Document Language
In the United States, workplace documentation language requirements reflect the legal framework and linguistic diversity of the workforce. Understanding these requirements helps ensure effective communication and workplace safety while protecting employee rights.
OSHA Requirements
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) explicitly requires that all safety training and information be provided in languages employees can understand. This includes Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and critical training materials. Failing to provide safety communications in accessible languages can result in workplace injuries and regulatory penalties.
State and Local Requirements
State and local jurisdictions often impose additional language requirements. Many states require employment rights notices to be posted in multiple languages when a significant portion of the workforce isn't proficient in English. California, Texas, and Florida have specific provisions given their large multilingual populations.
EEOC Considerations
The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission considers English-only workplace policies potentially discriminatory unless employers can demonstrate a clear business necessity. Companies must be particularly vigilant about safety documentation. If you employ workers who aren't fluent in English, you're legally required to provide safety information in their primary language.
Employers should consider their workforce demographics when determining which languages to use, though some state regulations may set specific thresholds for when translations become mandatory.
Evaluate Factors That Influence Language Choice
When determining the language for workplace documentation, three critical factors shape your decision-making process: workforce demographics, legal compliance requirements, and safety considerations.
These factors help you create an effective multilingual communication strategy that serves all employees while meeting regulatory obligations.
Workforce Demographics
Your workforce's linguistic composition directly impacts document language choices. If you employ workers from diverse backgrounds, providing materials only in English may create barriers to understanding critical information.
In the construction industry, for example, a significant portion of workers don't speak English as their primary language, making multilingual documentation essential for effective communication. Consider the primary languages spoken by significant portions of your workforce when developing documentation strategies.
Legal Compliance
Legal requirements significantly influence document language decisions. The Equal Employment Opportunity Commission views English-only rules as potentially discriminatory, particularly if they disproportionately affect employees based on national origin.
You must demonstrate that any English-language requirements serve a legitimate business necessity rather than mere preference. While you can require English usage in specific situations, such as during emergency communications or customer interactions, these requirements must be carefully justified and clearly communicated to employees.
Safety Considerations
Safety documentation requires particular attention to language choices. Workplace safety incidents disproportionately affect non-English speaking workers, making accessible safety communications a priority.
To help prevent incidents, you must ensure safety protocols, emergency procedures, and hazard warnings are comprehensible to all employees. Manufacturing facilities often address this by providing safety instructions in multiple languages, ensuring all workers can follow critical safety procedures.
Implement Best Practices for Multilingual Documentation
Implementing effective communication strategies can help employers manage language diversity in the workplace while maintaining compliance and operational efficiency.
Assess Language Needs
Start by conducting a comprehensive language audit of your workforce. Survey your employees to understand their language proficiency levels and communication preferences. This assessment should identify which languages are predominantly spoken and what critical documents require translation.
Regular feedback from employees about their communication needs helps pinpoint gaps and maintain clarity across the board.
Translate Essential Documents
When translating workplace documents, prioritize quality and accuracy over speed. While automated translation tools might seem convenient, they often miss crucial cultural nuances and legal terminology. If you use AI-powered translation, ensure that a bilingual speaker reviews the documents thoroughly before finalizing.
Implementing appropriate workplace translation tools and a centralized translation management system can help maintain consistency. Establish regular review cycles to keep documents updated as regulations and workplace terminology evolve.
Provide Language Assistance
To effectively communicate with non-English speaking employees, create a robust language support system by designating bilingual employees as language champions who can assist colleagues with immediate translation needs.
Develop a centralized resource hub where employees can access translated documents, glossaries, and communication guidelines. Consider offering language training programs for those interested in improving their skills, especially in roles requiring frequent communication.
Using plain language and visual aids can further support day-to-day operations. Provide simplified English versions of materials alongside translated documents.
During important training sessions or events, such as open enrollment, arrange for professional interpreters. This ensures employees receive accurate information and helps to engage frontline workers.
Document all translation and interpretation services provided, particularly for disciplinary or safety-related matters, to demonstrate ongoing compliance.
Follow a Compliance Checklist for Document Language
Before implementing any changes, conduct a thorough audit of your workplace documentation to identify gaps and prioritize translation efforts. A systematic approach helps you catch compliance issues before they become legal problems.
Conduct a Document Audit
Start by cataloging every document that may require language compliance. This includes:
- Employee handbooks
- Safety manuals
- Training materials
- Policy documents
- Required workplace posters
- Internal communications
Once you have a complete inventory, review each document against the legal requirements in your jurisdiction.
Check federal requirements first, such as FMLA provisions for notices in languages employees can read. Then, verify state and local requirements, keeping in mind that many states now publish bilingual posters as standard practice.
As you work through the audit, document any gaps you find so you can address them systematically. Next, analyze your workforce demographics.
Understanding which languages your employees speak, what percentage uses each language, and which departments need immediate attention will help you prioritize your translation efforts where they matter most.
Build Your Implementation Plan
With your audit complete, develop a strategic translation plan that balances legal urgency with available resources. Prioritize documents based on two factors: legal requirements and safety implications. A hazard communication document outranks an employee newsletter, for example.
When selecting translation methods, match the approach to the document type:
- Legal and technical documents: Engage qualified professional translation services to ensure accuracy and reduce liability
- Routine communications: Consider AI-powered translation tools for speed and cost efficiency
- Safety-critical content: Use professional translation with bilingual review, never automated tools alone
Set clear timelines for completing priority translations and allocate budget accordingly. Remember that translation is an ongoing need, not a one-time project.
Maintain Ongoing Compliance
Establish a document management system to centralize all translated materials. Version control is essential here, as outdated translations can create as many problems as missing ones. Set up regular review cycles to catch updates and ensure continued accuracy.
Build compliance into your regular operations by scheduling quarterly reviews of language requirements, creating a feedback channel for employees to report language-related issues, and documenting all translation decisions along with their rationale.
Maintaining records of workforce language demographics alongside corresponding document availability makes future audits far simpler and demonstrates good-faith compliance efforts.
Streamline Multilingual Document Delivery with Yourco
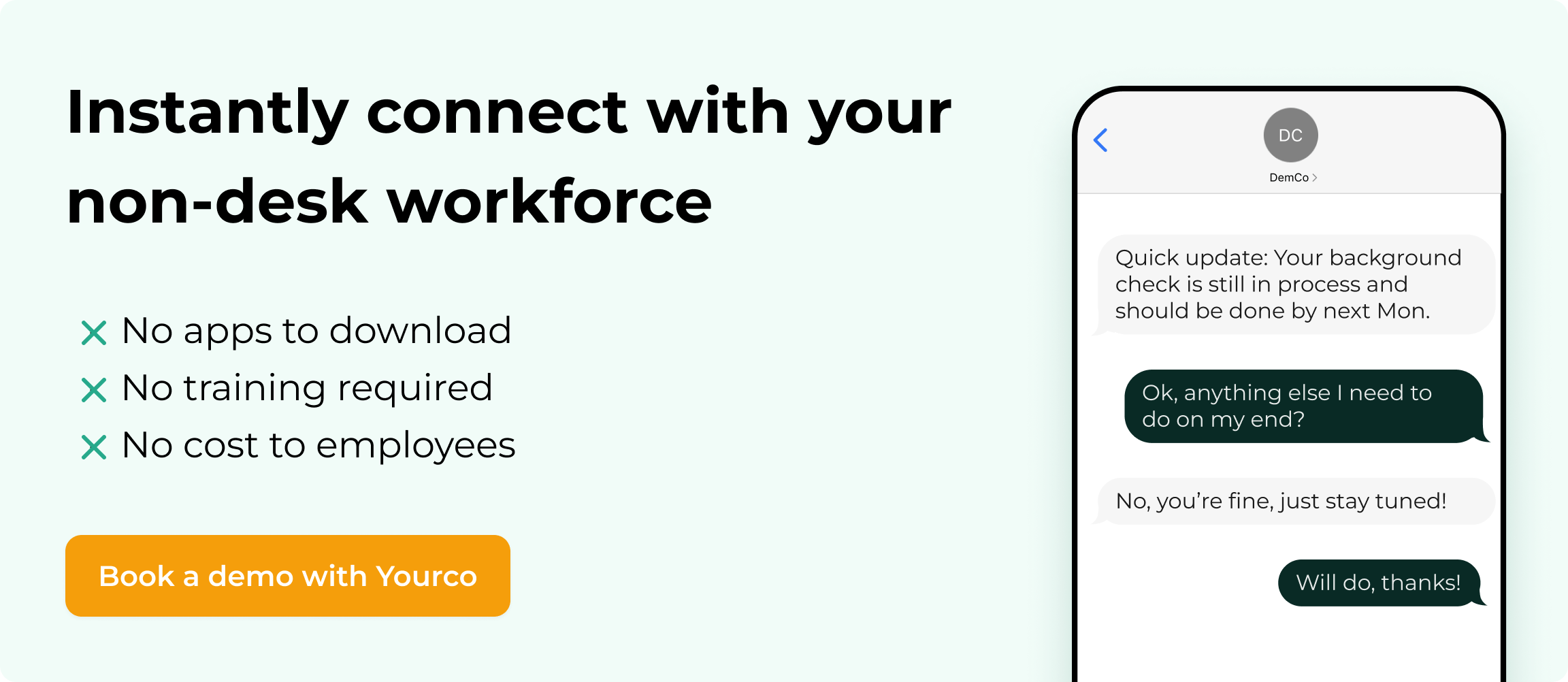
Delivering workplace documents in the right language is the first step toward creating a safe and inclusive environment, particularly for non-desk employees who may not have access to email or company intranets.
By combining robust language policies with direct, accessible communication channels, you can prevent misunderstandings and avoid legal pitfalls.
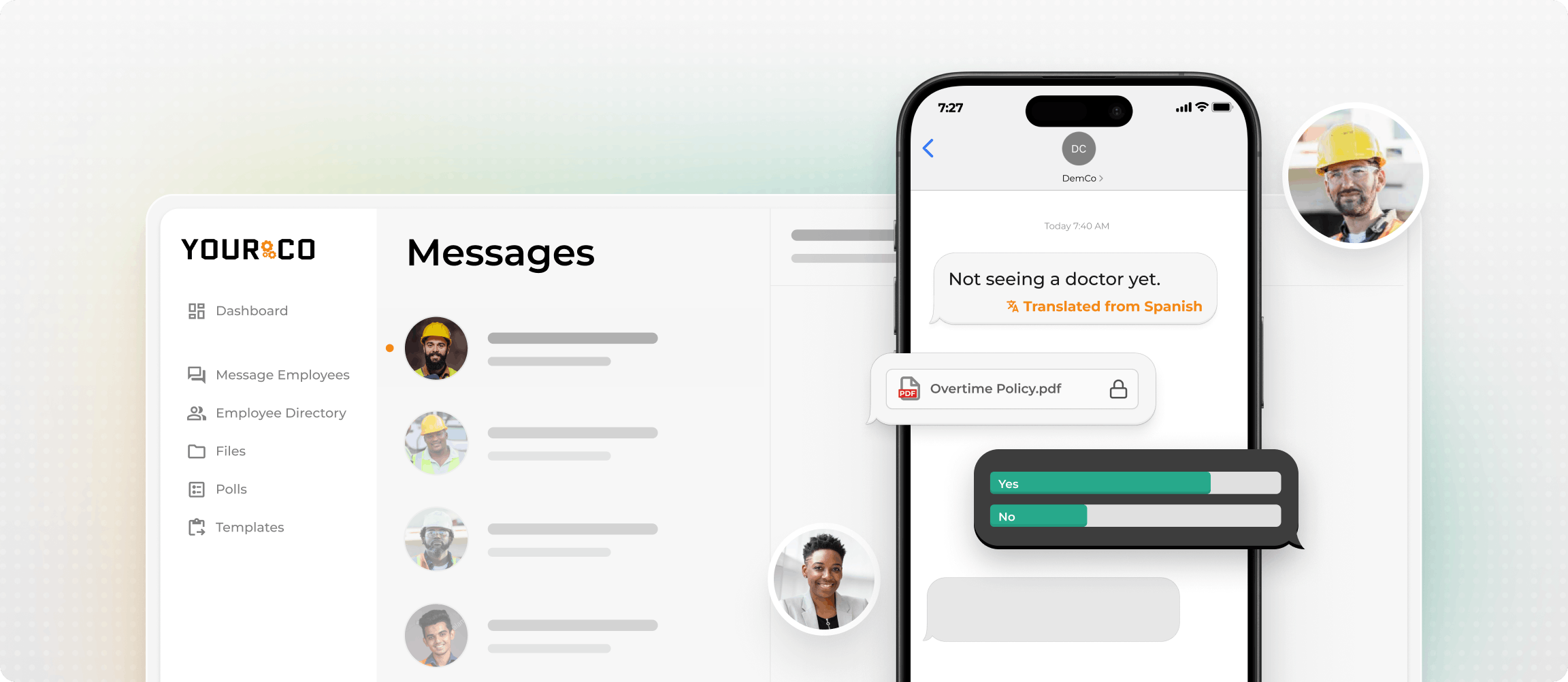
That's where Yourco excels. Built as an SMS-based platform for multilingual teams, Yourco provides an immediate, straightforward way to share crucial updates in over 135 languages and dialects.
Instead of managing expensive translation vendors or waiting for documents to be manually converted, Yourco's AI-powered translation automatically delivers messages in each employee's preferred language.
When you send a safety alert, policy update, or shift reminder, workers receive it instantly in the language they understand best. This automatic translation eliminates the delays and costs of traditional translation services while ensuring consistent, accurate messaging across your entire workforce.
Every message is time-stamped and stored automatically, creating a reliable record for audits and compliance reviews. From essential safety alerts to benefits information and beyond, Yourco keeps everyone on the same page and focused on what matters most: staying informed, productive, and safe.
Try Yourco for free today or schedule a demo and see the difference the right workplace communication solution can make in your company.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are employers legally required to translate workplace documents into other languages?
It depends on the document type and jurisdiction. OSHA requires safety training and hazard information to be provided in languages employees understand. Many states mandate multilingual postings when a significant portion of the workforce speaks a language other than English.
Employee handbooks and general policies don't always require translation under federal law, but providing them in employees' native languages reduces liability and improves comprehension.
Can I implement an English-only policy in my workplace?
English-only policies face scrutiny from the EEOC and may be considered discriminatory unless you can demonstrate a clear business necessity. You may require English in specific situations, such as during safety emergencies or customer-facing interactions, but blanket policies that restrict language use during breaks or casual conversations are difficult to justify legally.
Which workplace documents should I prioritize for translation?
Start with safety-critical materials, including emergency procedures, hazard warnings, and equipment operation instructions. Next, prioritize legally required postings such as wage and hour notices, anti-discrimination policies, and workers' compensation information.
Employee handbooks, benefits enrollment materials, and training documents should follow. Focus on documents where misunderstanding could lead to injury, legal liability, or significant operational problems.
How can I determine which languages my workforce needs?
Conduct a language audit by surveying employees about their preferred language for workplace communications. Review hiring records and note primary languages spoken. Pay attention to which employees struggle with English-only materials or frequently ask for clarification.
Some states set specific thresholds, such as requiring translated materials when 10% or more of employees speak a particular language.
What's the most cost-effective way to translate routine workplace communications?
AI-powered translation platforms offer the best balance of speed, cost, and accuracy for day-to-day communications like shift updates, policy reminders, and safety alerts.
These tools automatically translate messages based on each employee's language preference, eliminating per-document translation costs. Reserve professional human translators for legal documents, complex policies, and materials where errors could create significant liability.