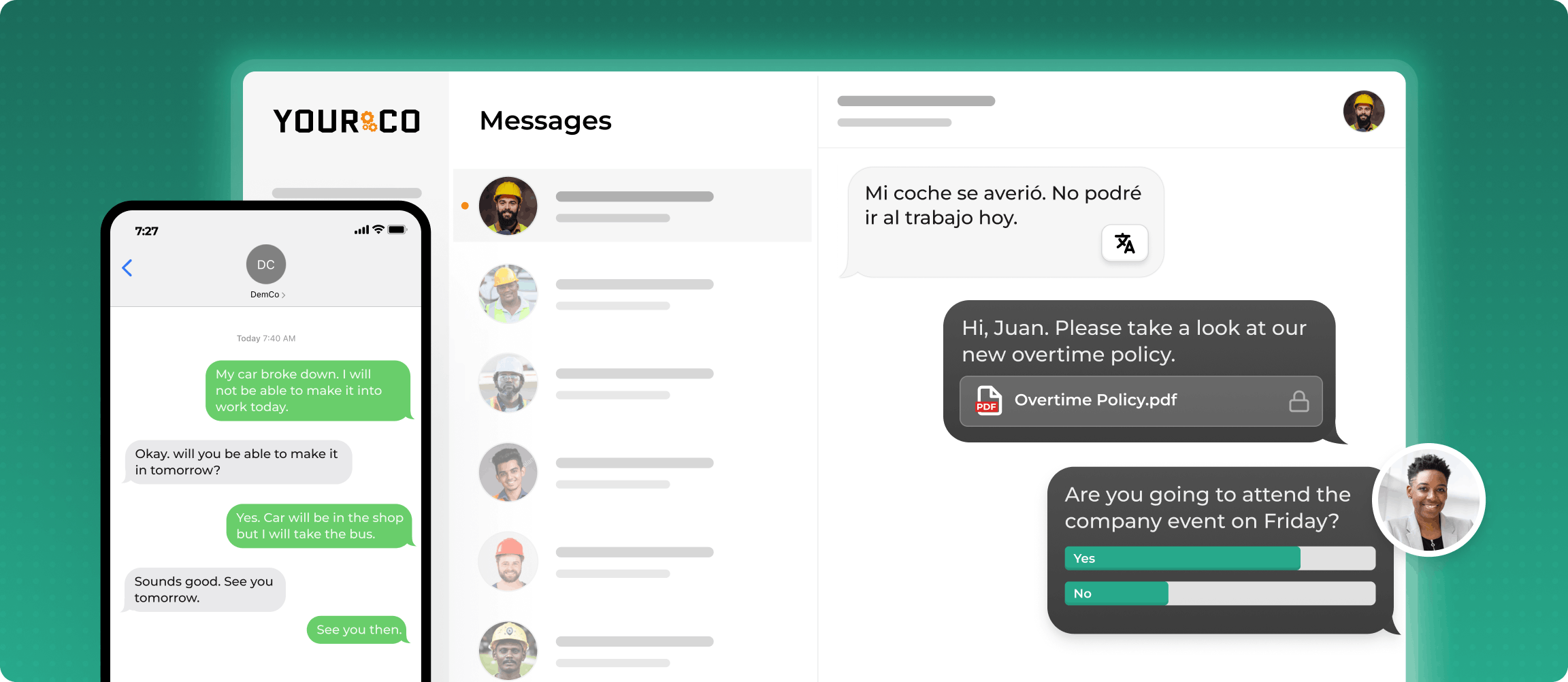
The facts speak for themselves. Unstable work schedules create psychological distress for 64% of affected workers, while consistent scheduling positively impacts productivity. Getting the right type of shift matters for everyone involved.
When you schedule work shifts, you do more than fill slots. You select the types of shifts that drive operations while keeping your team engaged and following the rules. Whether you run a 24/7 factory, handle seasonal retail rushes, or staff a hospital, your shift patterns directly affect both your results and how happy your people are.
This guide explores 15 different types of shifts modern organizations use. Each option offers unique advantages that might perfectly suit your specific needs. Smart shift management, combined with effective shift report formats, gives you a competitive edge beyond good operations.
1. Day Shifts
The first shift represents the standard daytime working hours, typically running from 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. or 7 a.m. to 3 p.m. This traditional shift forms the backbone of most business operations and remains the most popular shift among employees. Your office workers, retail staff, and light manufacturing teams thrive in this familiar rhythm.
Day shifts naturally align with your body's circadian rhythms, promoting better sleep quality and overall health. Your employees benefit from accessing support staff during peak business hours and arranging childcare more easily since most daycare centers operate during these times. The predictability helps everyone maintain consistent personal routines.
The downsides exist too. Your team faces rush-hour traffic during commute times, and if your business needs 24/7 operations, relying solely on day shifts creates coverage gaps that hurt your bottom line.
Regular breaks throughout the day combat afternoon fatigue; this simple wellness practice boosts productivity and reduces errors during slower post-lunch periods.
2. Second Shifts
The second shift, also known as the evening or swing shift, typically runs from 3 p.m. to 11 p.m. or 4 p.m. to midnight. This type of shift bridges the gap between standard day operations and overnight coverage, making it essential for businesses that need extended service hours. Evening shifts maintain operations during peak demand periods while providing seamless transitions to night coverage. You'll see this scheduling approach across industries that prioritize customer service and operational continuity.
Hospitality, call centers, manufacturing facilities, and healthcare organizations rely heavily on evening shifts. These sectors use second shift workers to handle increased evening demand and maintain consistent service quality throughout extended operating hours.
The second shift offers several compelling advantages. You can avoid the stress and delays of peak commute times, making daily travel more predictable and less frustrating. Evening shifts typically come with shift differential pay, providing additional compensation that makes these positions more financially attractive. Morning hours remain free for personal errands, medical appointments, and family responsibilities that would otherwise require time off from a traditional day shift.
However, evening shifts present unique challenges worth considering. The schedule often conflicts with traditional family dinner times and social activities, potentially straining personal relationships. Parents with school-aged children may find it particularly difficult to balance childcare responsibilities with evening work commitments. The transition between day and evening activities can also lead to fatigue issues without proper sleep schedule management. Additionally, evening shift workers often miss important company communications that occur during standard business hours.
From a compliance perspective, you should provide at least 8 hours of rest between the end of an evening shift and any subsequent work assignment. This rest period prevents fatigue-related safety issues and maintains productivity across shifts.
3. Third Shifts
The third shift, commonly known as the night shift or graveyard shift, typically runs from 11 p.m. to 7 a.m. or midnight to 8 a.m. This type of shift maintains essential operations during overnight hours when most of the population is sleeping. Healthcare facilities, security services, manufacturing plants with continuous production lines, and utilities that require round-the-clock monitoring rely heavily on third shift coverage. The overnight hours present unique operational challenges that require careful planning and specialized support systems.
Organizations typically offer the highest shift differential pay for overnight hours, often ranging from 10-30% above base wages, making financial incentives for third shift work the strongest among all shift types. The work environment tends to be quieter with fewer interruptions, less management oversight, and reduced workplace politics. Third shifts enable true 24/7 operations, maximize equipment utilization, and ensure critical services remain available when emergencies arise.
Third shift work comes with significant challenges that require careful consideration. Working against natural circadian rhythms increases risks for chronic diseases, sleep disorders, and metabolic issues. Night shift workers face higher accident rates due to fatigue-related cognitive impairment, and research shows increased psychological distress among workers with disrupted sleep schedules. Social isolation becomes a concern as night workers' schedules conflict with family and social activities.
Managers should protect night shift workers by implementing comprehensive fatigue management protocols. They should ensure adequate lighting, schedule regular breaks, provide healthy food options, and establish maximum consecutive night shift limits. Companies should consider rotating night shifts rather than permanent assignments to reduce long-term health impacts. Supervisors should monitor workers for signs of excessive fatigue and provide resources for sleep hygiene education.
Night crews face a critical communication gap with minimal management presence during overnight hours. Using a communication platform that allows scheduled messages for workers at all hours ensures that these workers are still kept informed no matter what time they clock in.
4. Fixed Shifts
Fixed shifts maintain consistent working hours and days each week with zero variation in schedule. These shifts can occur at any time, morning, afternoon, or evening, but their defining characteristic is complete predictability. Employees know their exact start time, end time, and days off weeks or months in advance, creating a foundation of reliability that benefits both workers and operations.
This predictability delivers several key advantages for your workforce. Employees can plan personal commitments with confidence, knowing exactly when they'll be working. Fixed shifts enable establishing consistent daily and weekly routines, which research shows improves both productivity and mental health. Parents particularly benefit from this arrangement, as they can secure consistent childcare that aligns perfectly with their predictable work hours. Additionally, schedule stability significantly benefits employee wellbeing by reducing psychological distress and improving sleep quality.
Fixed shifts do come with notable drawbacks. The lack of variation can create monotony over time, potentially reducing job satisfaction among employees who crave variety. They also offer limited flexibility for changing personal needs or preferences. Most concerning, employees assigned to unpopular shifts, such as permanent night or weekend shifts, may experience burnout without the relief that rotating schedules typically provide.
Fixed shifts work best for small teams or roles requiring consistent coverage, such as security positions or specialized technical roles.
5. Rotating Shifts
Rotating shifts move employees between day, evening, and night schedules according to a predetermined pattern. This approach ensures all team members share both popular and unpopular time slots equally, but requires skillful managing scheduling conflicts to maintain harmony. Weekly rotations might cycle workers from day to evening to night shifts each week, while complex arrangements like the 2-2-3 schedule deliver 24/7 coverage with predictable patterns.
The benefits make this system attractive for many operations. Rotating shifts distribute workload fairly across all time periods, give employees diverse work experiences, and help everyone understand operational needs during different hours. Your team develops better problem-solving skills when they've worked every shift.
The downsides require careful management. Constantly changing sleep schedules disrupt circadian rhythms, making it tough to establish consistent routines outside work. Physical and mental health can suffer over time as bodies struggle to adapt repeatedly.
Compliance demands attention to rest periods between rotations—maintain at least 11 hours between shifts.
Automated reminders help employees prepare mentally and physically for schedule changes. This preparation support reduces the stress of constant transitions and helps maintain better work-life balance during rotating periods.
6. Split Shifts
Split shifts break your workday into two separate periods with an unpaid break in between. Think working 7 a.m. to 11 a.m., going home for five hours, then returning for 4 p.m. to 8 p.m. Food service, transportation, education, and hospitality businesses use this approach to match staffing with customer demand patterns throughout the day.
This scheduling model shines when you need coverage during distinct busy periods. You can staff up for breakfast and dinner rushes without paying wages during slow afternoon hours. Employees often appreciate the extended midday break for personal appointments, errands, or even picking up kids from school. Some workers use the gap for a second job or side business.
The downside hits hard for many employees. Split shifts stretch the total time commitment to 12-13 hours from first start to final clock-out, despite paying for only 8 hours of work. Commuting twice daily gets expensive and exhausting, especially for workers who live far from the job site. The fragmented day can make planning personal activities difficult and leaves some feeling like they're always "at work" even during unpaid hours.
Compliance varies by state, with some requiring split-shift pay differentials to compensate for the inconvenience of returning after an extended break. Check your local labor laws before implementing this type of shift.
The biggest operational challenge with split shifts is second-period no-shows. Employees head home during the break and sometimes don't return for the evening shift. Using automated reminder texts sent as the break ends dramatically improves second-shift attendance and keeping your evening coverage reliable.
7. Flextime Scheduling
Flextime lets employees choose their start and end times within boundaries you set. Most companies include core hours when everyone must be present, balancing collaboration needs with individual flexibility.
This approach shines for creative, remote, or knowledge-based roles where results matter more than strict time tracking. Employees with flexible schedules adopt healthier lifestyle choices and see direct improvements in their overall well-being.
The benefits speak for themselves: better work-life balance, peak productivity during natural energy hours, and stress-free commutes outside rush hour traffic. The trade-offs include coordination challenges, potential coverage gaps during non-core hours, and more complex supervision when everyone works different schedules.
Flexible scheduling consistently boosts job satisfaction and retention, making it one of your strongest tools for keeping talent.
8. Compressed Workweeks
A compressed workweek lets you work full-time hours in fewer days, typically following patterns like four 10-hour days (4×10) or three 12-hour days (3×12). This scheduling approach works especially well in healthcare, emergency services, field maintenance, and utilities, where continuous coverage matters most.
The benefits speak for themselves: extended weekends, drastically reduced commuting costs and time, plus better work-life balance. Companies implementing compressed schedules often see a productivity boost and a reduction in absenteeism as employees appreciate the extra recovery time.
However, longer daily shifts can lead to fatigue, especially during those final hours of extended workdays. You'll also need to navigate potential overtime threshold issues and consider that caregiving responsibilities may become challenging during longer workdays. Managing scheduling issues like overtime thresholds and caregiving responsibilities becomes essential in compressed workweeks.
9. The 2-2-3 (Panama) Schedule
The 2-2-3 schedule, commonly called the Panama schedule, provides continuous 24/7 coverage through a specific rotation pattern: 2 days on, 2 days off, 3 days on, 2 days off, 2 days on, 3 days off. For detailed implementation strategies, see our comprehensive 24-hour coverage shift schedule guide. This pattern repeats every 28 days and typically uses 12-hour shifts with four teams rotating through the cycle. What makes this type of shift special is how it balances intense work periods with meaningful recovery time, creating a system that keeps operations running while giving employees predictable extended breaks.
This approach delivers clear benefits for both operations and workers. Teams enjoy consistent long weekends every other cycle, making personal planning much easier than traditional rotating schedules. The pattern distributes weekend coverage fairly among all teams, preventing the common problem where certain employees get stuck with permanent weekend duties. Workers also appreciate the predictability; once you learn the 28-day cycle, you can plan months ahead.
The 12-hour shifts do create challenges that need careful attention. Extended shifts can lead to fatigue, particularly during the three consecutive workdays in each cycle. New employees often need several cycles to adapt to the rhythm, and the handoffs between 12-hour shifts require thorough communication to maintain continuity.
Process manufacturing, healthcare facilities, and public safety operations favor Panama schedules because they need round-the-clock coverage without gaps. These industries benefit from the schedule's consistency; managers can predict staffing levels weeks in advance, and the extended shifts reduce the number of daily handoffs that can introduce errors.
Managing Panama schedules becomes much easier with automated communication systems. This creates a clear compliance trail while ensuring your teams stay informed about schedule changes without endless phone calls.
10. The 4-On / 4-Off Shift
The 4-On/4-Off shift pattern has employees working four straight days of 10-12 hour shifts, then taking four consecutive days off. Multiple teams rotate through this cycle to maintain continuous operations without coverage gaps.
This schedule delivers real benefits for your workforce. Those four straight days off give employees genuine time to recharge and handle personal commitments. The predictable pattern makes vacation planning simple since everyone knows their off periods well in advance. Weekend coverage gets distributed fairly across all team members, eliminating the usual complaints about unfair scheduling.
The challenges are worth considering too. Four consecutive long shifts can wear people down, especially when you're running 12-hour days. Handoffs between teams become critical communication points that can't afford to fail. You might also bump into overtime complications depending on how your pay periods align with the four-day cycles.
Manufacturing operations requiring continuous production, logistics companies, and emergency services rely heavily on this pattern. The extended coverage periods work well when stopping operations isn't an option.
11. Weekend Shifts
Weekend shifts cover Saturday, Sunday, or both when most businesses run with skeleton crews or need extended coverage. Common patterns include Friday-Sunday stretches (three 12-hour days) or Saturday-Sunday blocks (two 12-hour shifts), usually sweetened with premium pay to draw volunteers.
The benefits make weekend shifts attractive for both sides. You get coverage during traditionally tough-to-fill periods, tap into workers who can't commit to weekday schedules, such as students or parents, and the higher pay rates help attract quality staff. Retail stores, hospitals, manufacturing plants, and entertainment venues rely heavily on weekend coverage to serve customers or maintain operations.
The downsides hit hard though. Weekend workers sacrifice social time when everyone else is free, creating isolation and burnout. If someone already works a full weekday schedule, adding weekend hours can trigger FLSA overtime rules once they hit 40 hours. Plus, weekend staff often can't access HR, IT support, or other services that shut down after Friday.
12. On-Call Shifts
On-call shifts keep employees available to work on short notice during specified periods, though they won't necessarily work unless you actually need them. These arrangements walk a fine line between business flexibility and employee well-being, requiring careful attention to both response expectations and fair compensation. Workers typically receive standby pay even when not activated, plus premium rates when they respond to calls. The key lies in creating clear policies around availability and compensation that protect both your operational needs and your team's quality of life.
The biggest advantage is cost-efficient coverage for unpredictable situations. You can handle emergencies, equipment failures, or sudden demand spikes without maintaining full crews around the clock. This approach lets you scale your workforce based on actual needs rather than guesswork, keeping labor costs manageable while ensuring someone's always ready to respond.
The flip side creates real challenges for your employees. Workers face unpredictable income and must limit personal activities during standby periods, which can strain work-life balance over time. Legal complications around "engaged to wait" compensation add another layer of complexity; depending on how restrictive your on-call requirements are, employees may be entitled to regular wages for their entire standby period.
Industries like IT support, healthcare, emergency services, and utilities rely heavily on on-call coverage because rapid response to critical situations isn't optional.
13. Seasonal Shifts
Seasonal shifts exist for one simple reason: demand doesn't stay constant throughout the year. These temporary positions pop up during predictable busy periods like holiday shopping rushes, summer tourist seasons, or agricultural harvest times. Smart businesses use seasonal staffing to scale their workforce up and down based on these demand fluctuations.
The benefits make seasonal shifts attractive for many operations. You get perfect scalability for those predictable busy periods without carrying excess labor costs during slower months. Access to specialized seasonal talent often means finding workers who actually prefer temporary arrangements or have specific skills that align with peak seasons. Many college students, retirees, and parents with school-age children actively seek this type of work.
The challenges hit you where it hurts most: time and consistency. Recurring onboarding eats up management hours as you constantly bring new workers up to speed on procedures, safety protocols, and company culture. Quality can suffer when temporary staff lack the institutional knowledge that full-time employees develop over months or years. Maintaining that knowledge across seasonal transitions means documenting everything and hoping nothing falls through the cracks.
Retail explodes with seasonal hiring during holiday seasons, while agriculture depends entirely on harvest crews during specific months. Tourism businesses staff up for summer or winter seasons, tax preparation firms scramble during filing season, and construction companies adjust crews based on weather patterns and building seasons.
14. Part-Time Shifts
Part-time shifts typically involve fewer than 30-35 hours per week, distinguishing them from full-time positions in both structure and legal requirements. The Affordable Care Act's 30-hour threshold often influences how companies design these roles, since crossing that line can trigger benefit obligations that significantly impact labor costs. Forward-thinking businesses leverage this flexibility to their advantage, creating positions that attract workers seeking balance while meeting operational needs. Successful implementation requires managers to understand both the opportunities and challenges that accompany part-time scheduling.
These arrangements attract talent pools that traditional full-time roles can't reach. Students balancing class schedules, parents coordinating around family responsibilities, and semi-retired workers seeking flexibility all become viable candidates. Your company will reduce benefit costs while gaining the ability to scale staffing up or down based on demand patterns.
Effective managers must address certain trade-offs. Coordinating multiple part-time schedules instead of fewer full-time ones increases the risk of coverage gaps during peak periods. Part-time workers often view these positions as stepping stones rather than career destinations, leading to higher turnover rates. Matching employee preferred hours significantly improves retention and job satisfaction, making this alignment crucial for success.
Retail, hospitality, education, healthcare, and administrative support industries rely heavily on part-time models.
15. Overtime and Double Shifts
Overtime and double shifts involve working beyond regular scheduled hours, either by extending a current shift or working two consecutive shifts back-to-back. This approach provides instant coverage when facing unexpected staffing shortages or sudden demand spikes.
Organizations gain immediate benefits: extra capacity without the time and expense of hiring new employees, while workers earn premium pay rates, typically time-and-half under federal law. These arrangements provide essential coverage when employees call out sick or emergencies arise, keeping operations running smoothly during critical periods.
Extended work hours create significant challenges, though. Fatigue dramatically increases error rates and workplace accidents, while premium wages can strain labor budgets. The Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) requires overtime pay for hours exceeding 40 per week, and some industries have specific maximum hour limitations. Managers must carefully monitor these limitations to avoid legal violations and ensure compliance with overtime rules.
Healthcare facilities, emergency services, manufacturing plants during peak demand, and seasonal operations commonly rely on overtime scheduling. Success depends on ensuring adequate rest periods between shifts to maintain both safety and compliance.
Build Smarter Schedules That Actually Work
We’ve just explored 15 distinct types of shifts, each with unique strengths and challenges. The real magic happens when you stop searching for the "perfect" schedule and start combining different approaches strategically. Effective scheduling isn't about finding a one-size-fits-all solution; it's about creating a system that serves both your operational needs and your team's well-being.
Your step-by-step approach to building schedules that work:
Understand Your Operational Requirements: Dig into your business demands and peak periods using historical data. Identify when you need maximum coverage versus when smaller teams can handle the load. This foundation prevents both overstaffing and dangerous coverage gaps.
Gather Employee Input: Employee-centered schedule design directly impacts well-being and productivity. Survey your team about shift preferences, childcare needs, and work-life balance priorities. Their insights reveal scheduling blind spots you might miss.
Balance Workload and Skills: Distribute experienced workers across all shifts and ensure adequate coverage during challenging periods. Mix shift types strategically; fixed shifts provide stability for core operations while flexible arrangements support additional roles and create consistency where you need it most.
Consider Legal and Regulatory Rules: Stay compliant with overtime regulations, rest period requirements, and industry-specific guidelines. Proper shift management requires you to understand these constraints before you design schedules, not after problems arise.
Use Technology for Automation: Scheduling software streamlines complex decisions and improves communication across your entire workforce. For comprehensive guidance on leveraging technology for scheduling efficiency, explore our automated scheduling guide which covers advanced tools and best practices. Yourco's platform supports every aspect of this process through multilingual schedule reminders, real-time updates, employee feedback collection, and analytics that help you refine your approach continuously. The right combination of thoughtful shift patterns and effective communication tools transforms workforce management from a daily challenge into a strategic advantage.
Building Smarter Schedules with Yourco
While choosing the right shift patterns for your business is crucial for operational efficiency and employee satisfaction, managing these schedules can be a complex and time-consuming process. From handling compliance to ensuring communication between teams, these challenges can be overwhelming without the right tools in place. This is where Yourco comes in.
Yourco's SMS-based platform helps businesses streamline shift management by offering real-time communication, automatic shift reminders, and easy scheduling updates. For organizations with non-desk employees, such as those in manufacturing, logistics, and healthcare, Yourco’s ability to send multilingual messages ensures that all employees, regardless of their tech access, are kept informed and engaged. Whether it's scheduling reminders, work availability updates, or shift changes, Yourco’s communication system guarantees that no one is left out of the loop.
Additionally, Yourco’s automation tools can eliminate the administrative burden of shift management. By scheduling automatic messages and collecting feedback from employees through polls and surveys, businesses can continuously refine their approach to workforce scheduling. This not only improves operational efficiency but also enhances employee satisfaction by aligning schedules with their preferences and reducing common scheduling conflicts.
As your business adapts to changing workforce needs and operational requirements, Yourco offers the flexibility and scalability to meet these challenges head-on. The platform’s secure, user-friendly interface, combined with its powerful automation and communication capabilities, enables businesses to create dynamic shift schedules that meet both operational goals and employee needs. With Yourco, smarter scheduling is not just a goal, but a reality that empowers your team and enhances productivity.
Try Yourco for free today or schedule a demo and see the difference the right workplace communication solution can make in your company.