Translation Mistakes That Put Your Non-Desk Workers at Risk: A Guide for HR Leaders


Communication breakdowns and translation mistakes in multilingual workplaces can have devastating consequences, particularly for non-desk workers who operate in high-risk environments like manufacturing floors, construction sites, and logistics centers. A single mistranslated safety alert or procedural update can lead to workplace injuries, regulatory violations, and costly operational disruptions.
The challenge is compounded by the fact that many of the global workforce comprises non-desk employees, many of whom speak different languages than their supervisors. Traditional translation methods, whether manual or basic automated systems, frequently fail to capture the nuanced, context-specific terminology essential for workplace safety and operational efficiency.
This guide explores the most common translation errors that endanger non-desk workers and provides HR leaders with proven strategies to eliminate these risks while maintaining seamless communication across language barriers.
Common Types of Translation Errors in Professional Settings
Translation mistakes in the workplace aren't just awkward—they can be downright dangerous. Being aware of these errors helps keep everyone informed and secure.
Literal Translation Failures
One of the most dangerous translation errors occur when systems translate words literally without considering workplace context. For example, the Spanish phrase "punto muerto" literally means "dead point" but in manufacturing contexts, it refers to a mechanical "dead center" position. Basic translation tools often render this as "dead point," creating confusion that can lead to equipment misuse or safety violations.
Technical Terminology Misinterpretation
Industry-specific jargon poses unique translation challenges that generic tools cannot address. Manufacturing processes, safety protocols, and equipment names require specialized vocabulary that standard translation services lack. When a maintenance alert refers to "torque specifications" or "lockout/tagout procedures," mistranslation can result in equipment damage or worker injury.
Cultural Context Omissions
Translation errors extend beyond language to cultural communication styles. Direct commands that work in English may seem rude or confusing when translated into languages that prefer indirect communication. Similarly, urgency markers like "ASAP" or "urgent" may not translate effectively, leading to delayed responses to critical safety alerts. Also, when it comes to internal communication, workers are more likely to ignore or misinterpret communications that don't align with their cultural communication norms.
Policy and Compliance Mistranslations
When company policies or legal guidelines are mistranslated, employees might get the wrong idea about their rights and duties. This can open up compliance issues and legal risks. A misinterpreted safety guideline, for example, could result in employees unknowingly skipping essential safety steps.
Temporal and Measurement Conversion Errors
Non-desk workers often receive time-sensitive communications about shift changes, deadline modifications, or emergency procedures. Translation systems frequently fail to properly convert time zones, date formats, or measurement units, leading to confusion and missed deadlines.
For instance, a warehouse receiving "tomorrow at 14:00" might see this translated as "tomorrow at 2:00" without AM/PM clarification, causing workers to arrive at the wrong time. Similarly, temperature warnings in Celsius might be incorrectly converted to Fahrenheit, compromising safety protocols in temperature-sensitive environments.
Impact of Translation Errors on Workplace Operations
Translation blunders can ripple through your organization, impacting safety, productivity, and employee morale:
- Workplace Safety Risks: If emergency procedures or safety instructions are misread due to poor translation, the consequences can be dire. For example, a mistranslated "do not enter" sign could lead someone into a hazardous area. Utilizing reliable emergency notification systems can help ensure messages are accurately delivered.
- Reduced Productivity: Employees may spend extra time decoding confusing messages. According to Forbes, language barriers can significantly slow down operations. Time wasted on clarifying instructions is time not spent on getting the job done.
- Lower Employee Engagement: Staff can feel left out or misunderstood due to poor translations, leading to disengagement. For instance, if a benefits update is mistranslated, employees might miss out on opportunities or feel undervalued.
These issues create a balancing act between swift communication and accuracy. Each mistake can lead to misunderstandings that affect the whole team.
Best Practices for Preventing Translation Errors
Keeping translation errors at bay requires a proactive and layered approach.
Implement a Multi-Layer Review Process
The most effective translation error prevention involves multiple validation steps rather than relying on a single automated system. Leading organizations implement three-tier review processes:
- Automated pre-translation: Begin with AI-powered translation systems that understand workplace context. Modern platforms analyze industry-specific terminology and previous successful translations to improve accuracy. However, automation should never be the final step.
- Human expert review: Engage bilingual employees or professional translators familiar with your industry to review all critical communications. Focus particularly on safety alerts, procedural changes, and emergency instructions. Create a review checklist that includes technical accuracy, cultural appropriateness, and clarity of instructions.
- Field testing and feedback: Test translations with actual workers before full deployment. This reveals practical issues that desk-based reviewers might miss. Establish feedback mechanisms that allow workers to report translation problems immediately and track these reports to identify recurring issues.
By combining AI efficiency with human oversight and real-world validation, you create a translation system that doesn’t just look accurate on paper—it works reliably on the floor, where clarity can mean the difference between a close call and a serious incident.
Establish Clear Communication Protocols
Standardized communication protocols reduce translation complexity and improve consistency across all workplace interactions. Develop templates for common communications and establish rules for technical terminology usage.
- Standardized messaging templates: Create pre-approved templates for routine communications like shift changes, safety alerts, and procedural updates. These templates should include specific terminology that has been professionally translated and tested. Update templates regularly as workplace terminology evolves.
- Technical terminology glossaries: Maintain comprehensive glossaries of industry-specific terms with approved translations. Include context notes explaining when different translations might be appropriate. Train all staff members who create communications to use these standardized terms consistently.
- Emergency communication protocols: Develop specific procedures for translating emergency communications, including pre-translated emergency messages and rapid review processes for urgent updates. Emergency communications should be tested regularly to ensure translation accuracy under pressure.
- Clear escalation procedures: Establish protocols for handling translation disputes or unclear communications. Workers should know how to quickly report translation problems and receive clarification without disrupting critical operations.
Clear communication protocols streamline translation and build trust. When every message follows a tested, consistent format, workers can act quickly and confidently, even under pressure.
Invest in the Right Tools and Training
Generic translation tools, such as Google Translate, often fail in industrial environments due to their lack of industry-specific vocabulary and contextual awareness. Invest in specialized platforms designed for workplace communication, particularly those serving non-desk workers.
Tools and Technologies for Translation
To build a truly safe and multilingual workplace, organizations need purpose-built technologies that combine automation, context awareness, and real-time feedback. Below are three categories to consider.
1. AI-Powered Translation Systems
Modern AI translation platforms for workplace environments offer significant improvements over generic tools. These systems learn from context, build industry-specific vocabularies, and adapt to organizational communication patterns.
- Contextual learning capabilities: Advanced platforms analyze previous communications to understand how specific terms are used in your workplace. They recognize that "breakdown" might refer to equipment failure in manufacturing but delivery issues in logistics, adjusting translations accordingly.
- Industry-specific training: Leading translation platforms offer specialized training modules for manufacturing, construction, healthcare, and logistics industries. These modules include pre-loaded terminology and common phrase patterns specific to each sector.
- Real-time accuracy improvements: Modern systems continuously improve translation quality by learning from user feedback and correction patterns. This creates a self-improving system that becomes more accurate over time.
By combining contextual understanding with industry-specific training and continuous improvement, AI-powered translation systems offer a scalable way to reduce miscommunication and improve safety across diverse, multilingual teams.
2. SMS-Based Multilingual Communication Platforms
SMS remains the most effective communication channel for non-desk workers, with 98% open rates and fast response times. Modern SMS platforms now offer sophisticated translation capabilities specifically designed for workplace communication.
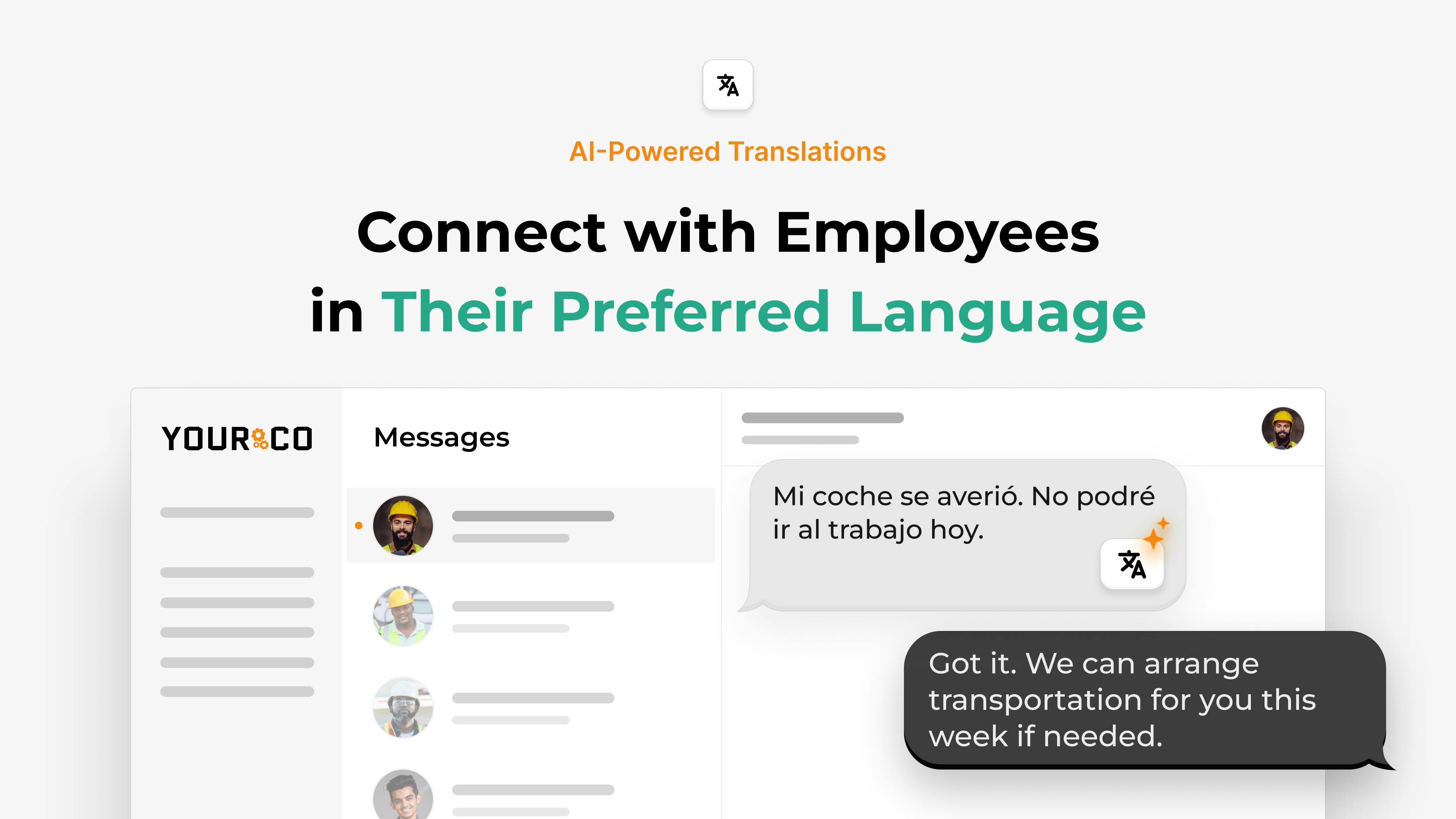
- Multi-language Support: Leading platforms, such as Yourco, support 135+ languages with specialized workplace terminology. They can automatically detect the recipient's preferred language and translate messages accordingly, ensuring consistent communication across diverse workforces.
- Bidirectional translation: Workers can respond in their native language, with responses automatically translated for supervisors. This creates true two-way communication without language barriers, improving feedback collection and emergency response capabilities.
- Compliance integration: Advanced SMS platforms maintain translation logs for regulatory compliance, showing exactly what information was communicated to each worker and when. This documentation is important for OSHA compliance and legal protection.
With built-in translation, two-way messaging, and compliance tracking, modern SMS platforms bridge the communication gap for frontline teams, ensuring that every worker receives critical information clearly, quickly, and in the language they understand best.
3. Quality Assurance and Testing Tools
Implement systematic quality assurance processes to identify and correct translation errors before they reach workers. This includes both automated testing and human verification systems.
- Automated quality checks: Use tools that automatically flag potentially problematic translations, including technical terms that might be incorrectly translated, cultural context issues, and formatting problems that could cause confusion.
- User feedback systems: Establish simple mechanisms for workers to report translation problems immediately. This might include reply-based feedback systems or dedicated hotlines for translation concerns.
- Regular translation audits: Conduct quarterly reviews of translation accuracy, focusing on frequently used communications and recent error reports. Use these audits to update terminology glossaries and improve translation protocols.
Quality assurance tools create a crucial safety net, catching errors before they cause confusion on the floor. When combined with worker feedback and regular audits, they turn translation into a continuous improvement loop.
Developing a Translation Error Management Strategy
Crafting a solid strategy involves careful planning and consistent effort.
Risk Assessment and Prioritization
Not all translation errors carry equal risk. Develop a systematic approach to identifying and prioritizing the most critical communication types that require the highest translation accuracy.
- Safety-critical communications: Prioritize perfect translation for all safety-related messages, including emergency alerts, equipment shutdown procedures, and hazardous material handling instructions. These communications should receive the most rigorous review and testing.
- Operational communications: Focus on accuracy for scheduling changes, procedural updates, and performance feedback. While not immediately safety-critical, these communications significantly impact productivity and employee satisfaction.
- Informational communications: General announcements, benefit updates, and company news require accurate translation but can tolerate minor errors without immediate operational impact.
By clearly ranking communication types by risk, organizations can focus their translation efforts on protecting worker safety first, then supporting smooth operations and engagement across the board.
Incident Response and Learning
When translation errors occur, systematic incident response and learning processes prevent recurrence and improve overall communication quality.
- Immediate response protocols: Establish procedures for quickly correcting translation errors and notifying affected workers. This includes emergency communication channels and rapid correction distribution methods.
- Root cause analysis: Investigate each translation error to identify underlying causes, whether system limitations, training gaps, or process failures. Use this analysis to improve prevention strategies.
- Continuous improvement: Regularly update translation protocols based on error patterns and worker feedback. Create feedback loops that allow frontline experiences to inform communication strategy improvements.
Treating translation errors as learning opportunities helps build a safer, more resilient communication system.
Training and Development Programs
Invest in comprehensive training programs for all staff members involved in multilingual communication, from message creators to translators to frontline supervisors.
- Communication creator training: Train HR staff and supervisors to write clear, translation-friendly messages. This includes using simple sentence structures, avoiding idioms, and clearly defining technical terms.
- Translator development: Provide ongoing education for internal translators about industry terminology updates and cultural communication preferences. Include training on new technologies and translation best practices.
- Frontline supervisor training: Ensure supervisors can recognize translation problems and know how to quickly address them. This includes understanding when to escalate issues and how to provide immediate clarification to workers.
Well-trained teams are the foundation of effective multilingual communication. Empower everyone to prevent errors and respond with confidence.
Strengthening Your Communication with Yourco
Effective communication is the backbone of any successful operation, especially when your workforce is diverse and always on the move. Translation errors shouldn't stand in the way of safety, productivity, or employee engagement. That's where Yourco comes in.
Yourco offers an SMS-based platform designed to streamline communication with your non-desk employees. Our service ensures that important messages are accurately delivered and easily accessible, bridging language barriers effortlessly. With features like customizable translations and centralized messaging, you can communicate crucial information without the risk of misinterpretation.
Imagine sending out a safety update and knowing every team member receives it clearly, no matter their preferred language. Or sharing policy changes with confidence that everyone understands their rights and responsibilities. Yourco makes all of this possible, enhancing connection and clarity across your workforce.
Try Yourco for free today or schedule a demo and see the difference the right workplace communication solution can make in your company.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common translation errors impacting non-desk workers, and how do they specifically affect workplace safety?
Translation errors that commonly impact non-desk workers generally arise from literal translation failures, technical terminology misinterpretation, cultural context omissions, and temporal or measurement conversion issues. These errors have specific implications for workplace safety.
For instance, literal translation failures occur when automated systems translate without contextual understanding, leading to incorrect instructions that can cause machinery misuse or improper safety procedure application. This creates a direct risk of accidents in environments such as manufacturing floors or construction sites where precise language is critical.
Furthermore, technical terminology errors, where industry-specific jargon is mistranslated, can result in workers misapplying technical procedures or product specifications. This misapplication can lead to equipment failures or unsafe handling of materials.
Additionally, cultural context omissions may lead to misunderstandings in communications that require urgent action, as different cultures have varying norms for urgency and politeness. Finally, errors in temporal and measurement conversions can cause workers to miss critical safety meetings or deadlines, posing risks to operational safety and efficiency. These translation errors not only endanger physical safety but also impact regulatory compliance, which requires safety protocols to be communicated accurately in workers' native languages.
How can HR leaders develop a robust translation error management strategy to prevent workplace accidents and regulatory non-compliance?
HR leaders can establish a strong translation error management strategy by focusing on detailed planning and continuous improvement processes. One effective approach is to conduct a thorough risk assessment to pinpoint critical areas where accurate translation is vital, such as in safety communications and operational updates. Prioritizing these communications ensures that any potential errors are minimized in high-risk situations, thereby reducing workplace accidents and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Additionally, creating a feedback-rich environment is essential. HR leaders should implement regular audits and establish feedback loops through which non-English-speaking workers can report translation issues quickly. By encouraging frontline workers to provide real-time feedback on translation quality, organizations can continuously refine their communication processes and tools.
This proactive approach not only helps identify recurring problems but also empowers workers by giving them a voice in the communication process. Furthermore, investing in ongoing training programs for staff involved in multilingual communication can bridge knowledge gaps and enhance the overall effectiveness of translation tools and protocols.
What role do AI-powered translation systems play in improving communication accuracy for non-desk employees, and how do they adapt to industry-specific jargon?
AI-powered translation systems play a crucial role in enhancing communication accuracy for non-desk employees by leveraging advanced technologies designed specifically for workplace environments. Unlike traditional translation methods, these systems utilize machine learning algorithms that can analyze vast datasets of industry-specific communications, enabling them to understand and translate complex, sector-specific jargon effectively.
These platforms are trained to recognize context, which is essential in accurately converting technical terminology and expressions that are unique to particular industries such as manufacturing, construction, and logistics.
Moreover, AI-powered translation systems constantly learn and adapt from user feedback and real-world application, which improves their translation accuracy over time. By incorporating user corrections and patterns in communication, these systems become increasingly sophisticated, ensuring that translations maintain safety and operational standards. They are also capable of real-time adjustments, allowing immediate response to feedback from non-desk workers, ensuring that the nuances and technicalities of the language used in these high-risk environments are correctly understood and communicated.
This adaptability not only helps in preventing potential workplace accidents due to miscommunication but also aids in maintaining compliance with industry regulations by ensuring that safety information and procedures are accurately conveyed in workers' native languages.
What are the best practices for integrating translation tools into existing communication systems to ensure consistency and effectiveness across diverse workforces?
Integrating translation tools into existing communication systems effectively requires a strategic approach that ensures both consistency and effectiveness across diverse workforces. One best practice is to conduct an initial audit of existing communication channels and workflows to identify gaps or inconsistencies in language use and translation needs. This helps pinpoint areas where integration will be particularly beneficial and outlines the technical and operational adjustments necessary for seamless tool adoption.
Moreover, it is important to choose translation systems that are flexible and adaptable to your organization's specific technological environment. Look for tools that can seamlessly integrate with your current HRIS, messaging apps, or employee communication platforms without requiring excessive modification. Ensure the selected tools can handle bidirectional communication, providing accurate translations for both outgoing messages and incoming responses, thereby maintaining dialogue consistency.
Regular training and updates are also crucial, empowering staff to fully leverage these tools and adapt to technological improvements or changes in industry-specific terminology. Finally, implement ongoing monitoring and feedback systems to assess translation tool performance, ensuring continuous improvement and resolution of any issues that may arise, thereby maintaining high communication standards across the board.
How can organizations establish clear communication protocols and escalation procedures to handle translation-related disputes and ensure timely clarification?
To establish clear communication protocols and effective escalation procedures for handling translation-related disputes, organizations should start by developing standardized templates for common communications. These templates should include pre-approved, context-specific terminology to prevent misunderstandings. Regular training sessions for both message creators and frontline supervisors can ensure that everyone understands these standardized terms and how to use them effectively.
For escalation procedures, companies should establish a clear, straightforward process for reporting and addressing translation errors. This could involve setting up dedicated communication channels such as a hotline or a specific email address for immediate assistance. Encouraging a culture where workers feel comfortable reporting issues without fear of reprimand is also crucial.
Providing feedback mechanisms allows employees to highlight recurring translation problems, helping the organization to continuously refine communication protocols. Regular audits and feedback loops can assist HR leaders in identifying and rectifying common translation issues, thereby improving overall communication quality and preventing future disputes.